Matter
* school science chemistry1. Definition
- Matter is anything that has mass and takes up space. THIS IS IMPORTANT
- All matter is composed of tiny particles
- Anything that has particles is matter. If you can trap it in a jar, it is matter.
2. Mass, Weight, and Volume
- Mass is the quantity of matter contained in an object. Weight takes into account gravity.
Volume is the amount of space occupied by matter. It is calculated by
\[W \times L \times H\]
3. Particle Theory of Matter
3.1. Five Core Principles of the Particle Theoryg
- All matter is made of particles with space between tem
- Different substances are made of different particles
- Particles are in constant random motion
- Particles of a substance move faster as temperature increases
- Particles are attracted to eachother
3.1.1. This can be represented in STAMP
- S = All matter is made of partices with space between them
- T = As temperature increases, particles move faster
- A = particles are attracted
- M = Particles are always moving
- P = Different substances are made of different particles.
4. Physical & Chemical Properties of Matter
4.1. Chemical Properties:
Chemical properties describe a reaction.
"Paper burns"
4.2. Physical Properties
Physical Properties describe physical traits of the substance itself. Can be quantitative and qualitative
The table is 3 metres long.
4.2.1. Qualitative Properties
Qualitative properties can be observed with the 5 senses, eg: "This computer is long"
| Term | Definition |
|---|---|
| Lustre | Shineness |
| Clarity | Ability to allow light through |
| Brittleness | Breakability or crumbly |
| Viscosity | Ability to flow or pour |
| Hardness | Relative ability to scratch or be scratched by another substance |
| Malleability | Ability to be hammered into a sheet or molded. Coming from 'mallet'. |
| Ductility | Ability to be drawn into a strand |
| Electrical Conductivity | Ability to allow electrons to flow through |
4.2.2. Quantitative Properties
Quantitative properties use a measurement. eg: "This computer is 5cm long"
| Term | Definition |
|---|---|
| Length | Measurement or extent of something from end to end |
| Volume | The amount of space occupied by matter |
| Mass | Amount of matter in an object |
| Temperature | The degree of hotness or coldness in an object. |
5. States of matter
5.1. Solid
5.1.1. Particle Behavior
- Strong attraction, hold particles close together
- Little space between particles
- Small movement(in place)
- Maintains shape
5.1.2. Temperature
- Low temperature(low energy)
5.2. Liquid
5.2.1. Particle Behavior
- Less attraction, particles can slide past each other
- Particle still close together, but able to move past and around each other
- More movement (past and around other particles)
- More of a "fluid" shape–Takes the space of container
5.2.2. Temperature
- Medium temperature (some energy added to system)
5.3. Gas
5.3.1. Particle Behavior
- Far apart–Low attraction
- Particles spread far around
- Lots of movement (past and around other particles)
- Takes space of container
5.3.2. Temperature
- Hotter
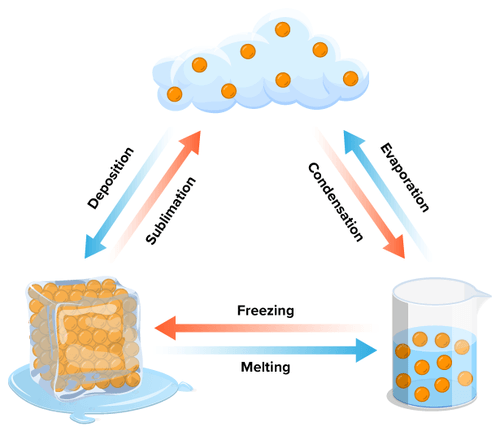
5.4. Changing states of matter
When we change from one state to another energy is either aded to or released from the systeml. This change in energy is what causes the change in particle behavior to which resuts in the change of state.
5.5. Pure Substances and Mixtures
One of the main ideas of the particle theory is that different substances are made up of different particles. We can therefore talk about 2 main types of substances:
5.5.1. Pure substances are made of particles that are all the same
- One type of particle
- Elements
Elements are elements of the period table – Just hydrogen atoms in hydrogen gas. It is still an element if it is the same atom. Particles that cannot be broken down into simpler different substances are called elements. Te smallest unit of an element is called an atom.
H, H2, Gold, SIlver, Oxygen etc-the elements can be found on the periodic table.
- Compounds
Pure substances that can be broken down into different Elements are called compounds..Compounds are elements bonded together– Like water. Made up of multiple atoms bonded together.
H2O
5.5.2. Mixtures are made of particles that are diferent(cntains at least two different types of particles)
- Many different types of particles
- Solution(Homogenous)
In a solution, you cannot differentiate the different particles by looking at it. An example of this is air, which is a solution of air, carbon, nitrogen, … (see: The atmosphere). If a substance does not stay homogenous for a long time, it is considered heterogenous This rule applies to things like milk/blood. After they spoil, you can see the seperate parts. Examples of solutions include: #+beginquote Salt Water, Brass, air, vinegar. #+endquote>
- Mechanical Mixture(Heterogenous)
- In a mechanical mixture, you an see the different substances. Examples include: #+beginquote
Granola bar, pizza #+endquote>
